Transportation as a Service or TaaS refers to on-demand rides and vehicle sharing without the hassles of car ownership. It also involves e-commerce and online delivery.
In this article, we will discuss the various aspects of TaaS and discuss its potential in altering the transportation sector.
Over the past fifty years, the transport industry has undergone a metamorphosis. The rise of autonomous cars, electric cars, and on-demand rideshares marks a considerable mobility shift. On-demand companies like rideshares are a current rage these days, and this phenomenon is also known as transportation As a Service (TaaS). Due to the convenience quotient, cost-effectiveness, and eco-friendly nature. It puts an end to the hassles of current vehicle ownership and lets the commuter choose a pay-as-a-use model.
Hence, TaaS is all set to be the next big thing, completely transforming the future of mobility. In this article, we will understand the working of the TaaS model and see if it is a worthwhile investment.
What Is TaaS?
TaaS is the acronym for Transportation-as-a-Service. If you’ve ever hailed a cab through a ridesharing app, you’ve used TaaS. Through this, people can buy trips, miles, or experiences without owning or maintaining their own vehicle. Instead of car ownership, TaaS focuses on renting vehicles.
Technology companies like Uber and Lyft are the most prominent examples of TaaS. You can use a ridesharing app to hire a cab without current vehicle ownership when you need a ride. Eventually, TaaS is likely to lead to a decline in car ownership rates.

The global transportation as a service (TaaS) market is expected to grow to $3.2 billion by 2028, at a CAGR of 16.6% during the forecast period.1 Increasing demand for on-demand mobility services and the growing adoption of TaaS solutions among enterprises and consumers are significant factors driving this market’s growth.
Many consider transportation as a Service (TaaS) or Mobility as a Service (MaaS) to be the future of transportation. Currently, TaaS involves an app like Uber and a human driver, but things may gradually change. Goldman Sachs expects the first semi-autonomous car to become commercially available in just a few years.2
Four macro trends that will shape the future of TaaS are:
Four macro trends that will shape the future of TaaS are:
- Electrified vehicles (EVs): EVs are likely to boost TaaS. Goldman Sachs predicted all cars sold by 2025 would be electric. Also, by then, electric vehicles will become ten times cheaper to operate and maintain than fossil-fuel-powered ones, making them perfect for fleet buyers.
- Global connectivity: Global Connectivity refers to the ability of a larger population to have internet access. According to the UN, by 2030, every person is likely to have easy internet access, including digitally enabled services.
- The Gig Economy: More than one-third of US workers (36%) are a part of the gig economy. In 2020, the gig economy expanded by 33%, at 8.25x faster than the entire US economy. As a result, companies like Uber see an influx of drivers, ultimately leading to more rides and expansion.
- ESG investing: ESG investing has increased exponentially, and companies are more aware of this than before. They are becoming more environmentally and socially responsible. With Electric Vehicles as a vital component, TaaS is likely to benefit from this growth phase of ESG investing.
The TaaS market will grow thanks to ridesharing in personal transport, freight, food, and drone delivery and distribution exponentially.
How Does TaaS Work?
TaaS combines services from public and private transportation providers wherein a unified gateway creates and manages the trip, which users can pay for with a single account.
Uber introduced TaaS, which became a global phenomenon. Their business model is not incredibly capital-intensive because Taas companies don’t own cars in their fleet as they belong to personal vehicle owners. Instead, they operate on a fixed-cost model.
The TaaS companies incur a high cost for expansion, technological infrastructure, and customer acquisition. TaaS players enjoy a competitive edge over other traditional transportation companies in the form of capacity utilization. They use disruptive technology to match capacity and demand on a large scale. Over time, because of operating efficiency, its profitability grows.
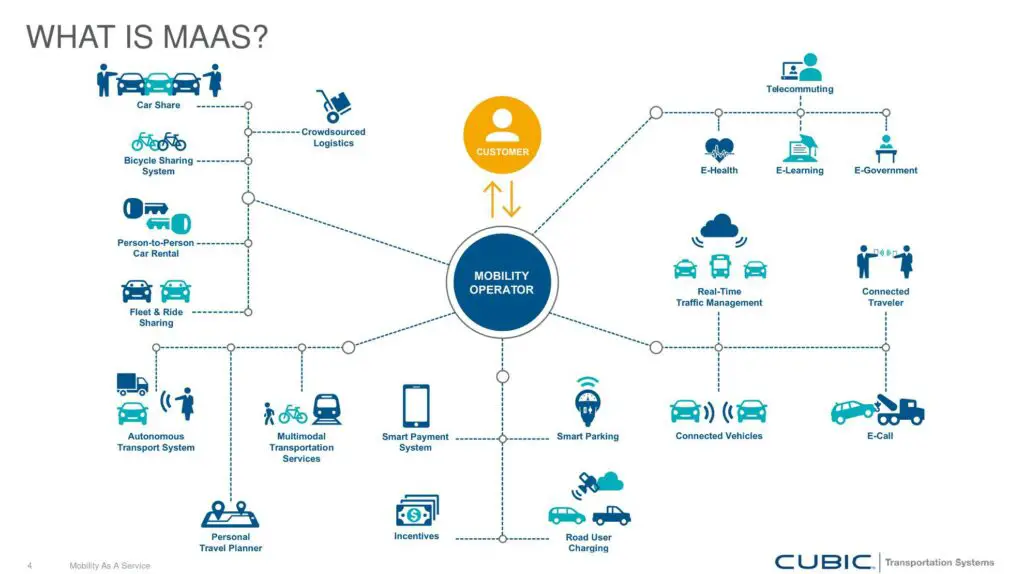
Interestingly, besides ridesharing, other TaaS business models include vehicle sharing. Companies can purchase a large fleet of small vehicles like scooters or bikes and deploy them over large Tier-I cities. With the help of their app, customers can use one of those vehicles and park it at the predetermined destination. After this, it can be available to another customer for use.
Another popular TaaS business model is Delivery-as-a-Service. Vehicle Owners can choose to deliver food from restaurants or packages to earn passive income in their spare time.
Benefits of TaaS
TaaS has several advantages that range from economic to social, geopolitical, and environmental. Here are some of the significant benefits of transportation as a service. (TaaS).
Safety
According to the US Department of Transportation, 10,412 people lost their lives in 2019 due to alcohol-impaired driving.3 TaaS could reduce the number of road accidents due to such unfortunate instances. Those under the influence of alcohol can book a car on demand instead of driving independently.
A report published by the Journal of American Medical Association (JAMA) has highlighted that motor vehicle collision traumas declined by 23.8% on Friday and Saturday nights for all ages in Houston after Uber began to operate.4
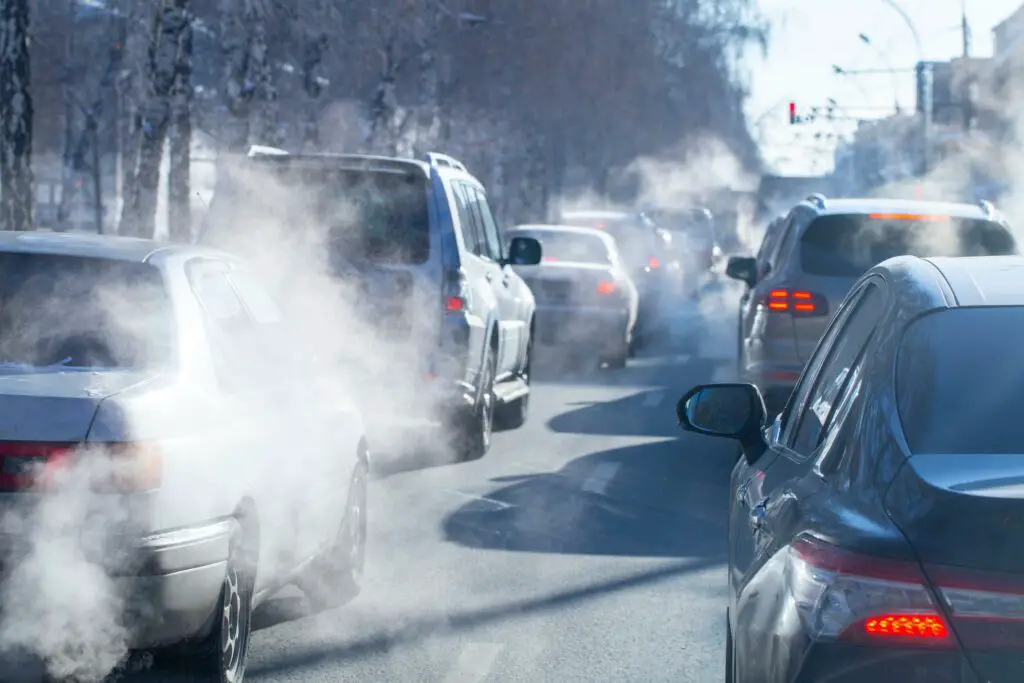
Lower Carbon Emission
Rising car ownership has caused many hazards, and air pollution is one. Air pollution is increasing dramatically due to the increased use of fossil fuels for energy. As per ITDP estimates, if the number of cars increases to 2 billion, it can be detrimental to our environment.5. However, if TaaS is used effectively, the number of vehicles can be reduced to 250 million by 2050, thus reducing carbon emissions.

Cost-Effective
Owning a car has a lot of additional costs, and you need to pay for car insurance, gas, maintenance costs, and car payments. By adopting TaaS, you can save a lot of vehicle costs, especially those related to car maintenance. According to Whitney Tilson, CEO of Empire Financial Research, TaaS will save 93% of American families $5,600 a year, dramatically lowering the cost of flights, cars, and houses.6
Free Space
TaaS has the potential to transform the urban landscape radically. As individual vehicle ownership reduces, there won’t be a need for parking or repair facilities. This will free up a lot of extra space, which the authorities can use for infrastructure development.
Factors Driving the Need for TaaS?
Several factors have led to the rise of TaaS. Some are them are:
Cars Are Expensive
Cars are costly, and it comes with extra maintenance expenses, sometimes on an average of about $9000 a year. The worst part? Some personal vehicles aren’t used 90% of the time, and cars sit parked in the garage’s driveway. As car ownership declines, it creates new opportunities for the transportation market to prosper.
Less Pollution
Combustion engines vehicles emit carbon dioxide and contribute about 20% of the air pollution in the United States. Rising awareness about global warming and climate change has led people to be inclined toward TaaS. Climate change is the crucial reason behind cars losing popularity and some cities banning diesel and combustion engine vehicles altogether.
Convenience
The adoption of mobile technology is one big reason driving the growth of TaaS. The acceleration of smartphone and mobile data penetration has enabled seamless travel and real-time information that only transportation as a service (TaaS) can provide.
Big Data Analytics
Today, a massive amount of data is available on traffic, transit patterns, road networks, seasonality, demand, and supply. TaaS companies analyze this enormous volume of information to determine the best round and help governments with infrastructure planning projects.
Ease in Monitoring
Car rental companies find electric vehicles easier to monitor as the car doesn’t need to be refueled conventionally. Moreover, electric vehicles are powered by sensors to provide information about their well-being and performance. This helps the car maintenance companies to manage an entire fleet of rentable electric cars through a single dashboard.

Drawbacks to Using TaaS
The future of TaaS is pretty attractive; however, we also need to evaluate the various drawbacks of this phenomenon. Some of the prominent ones are:
Economic Implications
The impact is not just restricted to the automobile sector but the entire ecosystem. Many ancillary businesses like repair, parking, spare parts, etc., may have to shut shop to fulfill the demands of the changing industry landscape of mobility. This is likely to impact the entire economy to a large extent. Many industries will be compelled to transform their structure and operations, leading them to invest a large sum of money, which they could also lose.
Congestion
When ridesharing services like Uber were newly launched, it was readily available and pretty affordable for the customers. But as time passed and Uber gained more popularity, more people signed up for it. This proved to be counterproductive. After a particular point, instead of reducing congestion on the roads, TaaS vehicles somewhat increased it, especially in tight areas. The research paper, How Do On-demand Ridesharing Services Affect Traffic Congestion, has enough empirical evidence to prove it.7 Carpooling lanes might be expanded to accommodate more shared-use vehicles.
Privacy Issues
TaaS has its foundation in using technology and data obtained from customers, and it is a data-driven service at the core. The seamless operations of the TaaS industry directly depend on the quantum of the available data. But this may also pose a severe threat to the users’ privacy.
Why Are Taas Stocks so Popular?
TaaS stock refers to any financial asset sold by a public company in the TaaS industry, like UBER, DoorDash, and Lyft. How to invest in TaaS stocks? You only need to open a brokerage account or download an investment app, and after that, you can start investing in any of these TaaS stocks.
There are several reasons why TaaS stocks have gained so much popularity. TaaS services are available almost 24/7 in most cities across the globe. According to a study by McKinsey and Morgan Stanley, over 111 million food delivery service users in the United States in 2020.8 This represents close to 30% of the entire US population, which means the growth potential is more considerable than it seems.
The sector is still in its infancy, and it holds a massive growth potential. Most TaaS sectors are based on the emergence of technologies like electric cars and autonomous vehicles. Both are futuristic concepts that are becoming a reality. These evolutions are set to integrate into the TaaS industry and propel its growth upwards.
No investment promises extraordinary returns, but it is pretty evident that the TaaS industry is all set for a boom, making it fertile ground for analysts smart enough to determine winners in the space.
While TaaS companies are revolutionary, most struggle with profitability. Intense price competition and zero product differentiation are the primary reasons behind it. Several big players incentivize customers through discounts and freebies to fuel growth, and scale, thus compromising profitability.
Successful Companies Providing Transportation as a Service
Two of the biggest companies in the TaaS sector are Uber and Lyft; however, many more companies are present in this sector in some form or the other. Some are pure TaaS players, while others only have a portion of their operations in the TaaS.
Some of the top TaaS stocks are:
Uber Technologies
Uber is one of the most prominent players in the TaaS industry. Its services include ridesharing, food delivery, courier services, and bicycle and scooter hire. In the ridesharing market in the US, Uber holds a dominant position controlling over 65% of the market. Its services are now available across 71 countries and 10,000 cities. It has a 12-month revenue of nearly $14.8 billion and a current market cap of $80.53 billion.
Doordash
DoorDash is USA’s most comprehensive online food-delivery platform serving over 20 million customers across Canada and Australia. It was around 50% of the United States’ food-delivery market, serving 20 million customers across the US, Canada, and Australia. DoorDash has expanded its services to storefront and Self-Delivery, which is a positive sign for growth. It has a 12-month revenue of nearly $4.6 billion and a current market cap of $45.1 billion.
Lyft
Lyft’s services include ride-hailing, food delivery as well as bicycle hire. Currently, the company serves 644 cities in the USA, and it also has operations in about 12 cities in Canada. With over 30% market share, it is the second-largest ride-hailing service in the USA. Lyft’s technology partner is Aptiv, which delivered over 100,000 automated rides. Lyft’s stock plunged to an all-time low in March 2020; it rebounded strongly, posting a 300% over the next 12 months. It has a 12-month revenue of roughly $2.1 billion and a market cap of $14.05 billion.
Yandex
Yandex is a conglomerate providing digital consumer services across countries. The company manages several tech businesses, including e-commerce, electric vehicles, and digital payments across Russia, the Middle East, and Africa. These are high-growth markets, and TaaS is only one of its operations. It has a 12-month revenue of roughly RUB 317.4 million and a market cap of $18.7 billion.
Facedrive
Facedrive is a Canadian ride-hailing company offering eco-friendly modes of commute and delivery to customers using EVs. The company makes users aware of their carbon footprint and provides an option between EVs and gasoline vehicles.
The company also has a vehicle subscription service offering users electric vehicles on-demand. Facedrive, through its ECO-Cred, helps businesses and consumers purchase carbon offsets. Facedrive is a relatively new entrant, and it operates on a small scale; however, it has seen spectacular growth. The company has a market cap of CAD 87.7 million.
GATX Corporation
GATX is one of the oldest and most popular railcar lessors with a well-established system of railcars. In alliance with Rolls-Royce Limited, the company owns one of the largest aircraft spare engine lease portfolios. In May 2020, GATX sold its dry bulk vessel business, American Steamship Company, to Rand Logistics for $260 million. It acquired Trifleet Leasing Holding B.V., the world’s fourth-largest tank container lessor, in December 2020. The company had a market cap of $3.6 billion and twelve-month sales of $1.2 billion.
Impact of COVID-19 on TaaS
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a severe impact on several mobility systems. The demand for personal mobility hit an all-time low due to lockdowns, social distancing, and sanitization requirements. At the same time, operational complexity has increased.
COVID-19 virtually disrupted every aspect of the transportation industry. There has been a spike in the e-bike demand, whereas the shared scooters saw some initial struggle but rebounded later. As consumers turned to cards and other alternatives, the ridesharing aspect of TaaS took a hit. At the same time, we could witness an upsurge in demand for delivery and e-commerce.
During the lockdown, millions of people ordered food online for the first time. Food delivery apps like Uber Eats, DoorDash, and Deliveroo saw a massive acceleration in orders within the first three months of lockdown in 2020.

A report by Arthur D. Little suggests that over the short term, the COVID-19 crisis might negatively impact the scalability of TaaS because its business model is primarily based on mass transit trips.9 Due to collapsing demand, shared mobility modes have badly suffered.
TaaS is likely to strengthen the system’s resilience by offering more mobility options and ease of use in the medium term.
In the longer term, the development of TaaS B2B offerings could accelerate more adoption, as the willingness of companies to adopt flexible working hours or associate with transit operators has accelerated due to COVID-19.
The Bottom Line
Experts believe that TaaS is the third phase of the transport revolution after electrification and automation. It aims to address three significant problems: pollution, accessibility, and the number of cars simultaneously on the road.
TaaS has the potential to be a full-fledged industry within the next five decades or before that. As car ownership declines, TaaS will change the face of the transportation market. The return on investment from the TaaS sector is equally promising, and these returns are not just limited to profit. They can solve real-time problems that have created a detrimental impact on society. With proper investment planning and regulations in place, transportation as an industry or TaaS can bring about a revolution.
TaaS would require a more advanced long-term plan that the government and its authorities thoroughly back to realize its potential. Municipalities need to design strategic plans for low-cost transportation available to most people.
In the years to come, considerable developments in autonomous vehicles. Electric vehicles and connected cars will be a turning point for TaaS. Besides, Blockchain development is all set to modernize the transportation sector.
The ultimate vision of TaaS isn’t just about the autonomous or electric vehicle industry. Instead, it is a holistic concept that involves equal development of the entire ecosystem comprising on-demand rides, delivery, and shared mobility.